Q. Example of retail inventory method?
In Exhibit we display the retail inventory method. In the exhibit the costs (USD 22000) as well as retail (USD 40000) amounts for beginning inventory are available from the preceding period's computation.
The amounts for the first quarter purchase returns, purchases, purchase allowances and transportation-in came from the accounting records. The amounts for purchase allowances along with transportation-in appear only in the cost column. The first quarter sales amount (USD 280000) is as of the Sales account and stated at retail (sales) prices. The difference among what was available for sale at retail prices and what was sold at retail prices (which is sales) equals what should be on hand (March 31 inventory of USD 60000) expressed in retail prices. The retail price of the March 31 inventory requires to be converted into cost for use in the financial statements.
We do this by multiplying it times the cost / retail price ratio. In the instance the cost/retail price ratio is 60 percent which means that on the average 60 cents of every sales dollar is cost of goods sold. To discover the 2010 March 31 inventory at cost (USD 36000) we multiplied the ending inventory at retail (USD 60000) by 60 percent.
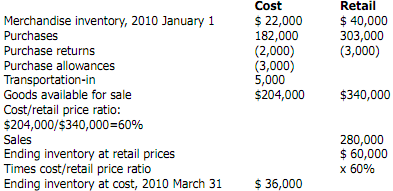
Formerly the March 31 inventory has been estimated at cost (USD 36000) we deduct the cost of the inventory from cost of goods available for sale (USD 204000) to determine cost of goods sold (USD 168000). We can as well find the cost of goods sold by multiplying the cost/retail price ratio of 60 percent by sales of USD 280000.
For the subsequent quarterly period the USD 36000 and USD 60000 amounts would appear on the schedule as beginning inventory at cost and retail respectively. We would embrace other quarterly data regarding purchase returns, purchases, purchase allowances and transportation-in to determine goods available for sale at cost and at retail. From these amounts we could calculate a new cost/retail price ratio for the second quarter.
At the end of each year merchandisers typically takes a physical inventory at retail prices. Ever since the retail prices are on the individual items while the cost is not taking an inventory at retail prices is more convenient than taking an inventory at cost. Accountants are able to do then compare the results of the physical inventory to the calculation of inventory at retail under the retail inventory method for the fourth quarter to determine whether a shortage exists.
Both the retail inventory and the gross margin methods can help you detect inventory shortages. To illustrate how you are able to determine inventory shortages using the retail method presume that a physical inventory taken at year end showed only USD 62000 of retail-priced goods in the store. Presume that utilize of the retail method for the fourth quarter showed that USD 66000 of goods must be on hand thus indicating a USD 4000 inventory shortage at retail. Subsequent to converting the USD 4000 to USD 2400 of cost (USD 4000 X 0.60) you would report this as a Loss from inventory shortage in the income statement. Knowledge of such shortages may perhaps lead management to prevent or reduce them by increasing security or improving the training of employees.