Basic Assumption of Transportation Model
The basic assumption of the model is that the transportation cost on a given route is directly proportional to the number of units transported. The "unit of transportation" will differ based on the "commodity" transported i.e. a truck load may be a better unit than single product units.
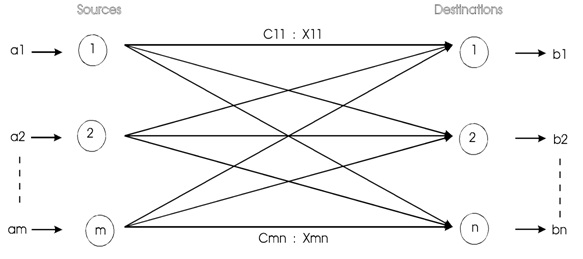
m = Source
n = Destination
A source or destination is represented by a node. The line joining a source with a destination represents the route through which the commodity is transported.
The quantity of supply at source i is ai and the demand at destination j is bj. The "unit" transportation cost between source i and destination j is cij
Let xij represent the amount transported from i to destination j.
The LP Model symbolizing the transportation problem is given usually as:
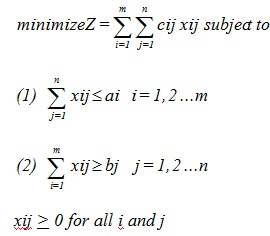
xij > 0 for all i and j
(1) It stipulates that the sum of the shipments from a source cannot exceed its supply.
(2) It requires that the sum of the shipments to a destination must satisfy its demand.
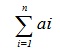
The model explained above implies that the total supply
must at least equal the total demand if the total supply equal the total demand then it is called a balanced transportation model. It differs from the above model in the fact that all constraints are equations.
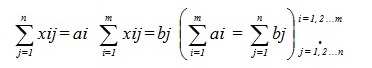
In actual life, this is not essentially true. Though, a transportation model can always be balanced. The balancing, in addition to its usefulness in modeling certain practical situations is important for the development of a solution method that fully exploits the special structure of the transportation model.