Reference no: EM13748388
1. The following signaling game is, ostensibly, about war and peace, but one could think of "war" as entering a potentially contested market, "peace" as not enter-ing, and "deadly" as an innovation in production that makes one a much more fearsome competitor. With probability ρ= 3/5, country l's secret military research program makes their armies deadlier (i.e. giving higher expected utility in case of war through higher probability of winning and lower losses), and with probability 2/5 the re-search project is a dud (i.e. making no change in the army's capacities). Knowing whether or not the research program has succeeded, country 1 decides whether or not to declare war on or to remain at peace with country 2. Country 2 must decide how to respond to the invasion, either fighting or ceding territory, all of this without knowing the outcome of l's research program. With payoffs, one version of the game tree is:
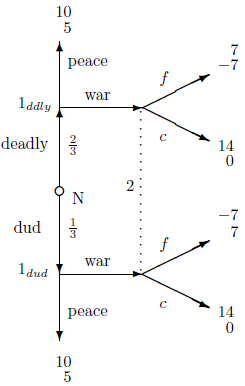
a. Show that it is not part of an equilibrium for 1 to invade when weak and stay out when strong.
b. Show that it is not part of an equilibrium for 1 to invade when strong and stay out when weak.
c. Show that there are no equilibria in which 1 strictly randomizes after both outcomes, deadly and dud.
d. Show that there are no equilibria in which 1ddiy strictly randomizes.
e. Show that there are no equilibria in which strictly randomizes.
f. Show that there are two sets of equilibria.
g. Show that there are no weakly dominated strategies.
h. Show that, relative to the set of equilibria in which 1 always stays out, war is dominated for ltd. Further show that deleting this makes f weakly dominated for 2, which means that none of the strategies in this set of equilibria can be played so that this set of equilibria fails the sequential self-referential test.
2. Discounting problems.
a. You take out a loan for L agreeing to payback at a rate x per year over the course of T yeas. Interest is continuously compounded at rate r so that L = 0∫T xe-rtdt.
i. Find the payback rate, x, as a function of L, T, and r. Explain the intuitions for why x should depend in the fashion that it does on these three variables.
ii. Find the necessary payback time T, as a function of x, L, and r. Explain the intuitions for why T should depend in the fashion that it does on these three variables, paying special attention to the case that there is no T solving the problem.
b. A project will cost 10 per year for the first three years, and then return benefits of 8 per year in perpetuity (i.e. for the foreseeable future). Throughout, suppose that interest is continuously compounded.
i. Find the internal rate of return (MR) on this project, that is, find the r for which the net present value is equal to 0.
ii. Find the payback time at interests rates of 10%, 20%, and 30%.
3. A software designer, s, and a marketer, m, form a partnership to which they contribute their efforts, respectively x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0. Both have quasi-linear utility functions, us = $s - x2 and um = $m - y2, where $s and $m are monies received by s and m respectively.
The strictly concave, twice continuously differentiable profit function Π satisfies Π(0, 0) = 0, is strictly increasing in efforts, ∂Π(x, y)/∂x > 0 and ∂Π(x,y)∂y > 0, and is strictly supermodular, ∂2Π(x, y)∂x∂y > 0. Throughout the following, assume that optima and equilibria are strictly positive.
a. Give the derivative conditions for the efficient choices of x and y, that is, for the x and y that maximize the sum of the utilities of the two partners.
b. Suppose that neither effort nor sidepayments are legally enforceable, that the partners choose their efforts simultaneously, and share the profits equally. Show that the equilibrium for this game is inefficient and explain why.
c. Suppose now that the software designer chooses her effort before the marketer chooses his, and the marketer observes the designer's effort before choosing his own. Again assuming that the partners share the profits equally, show that the equilibrium of this game is inefficient and explain why.
d. Show that the designer and marketer could pay a manager to design contracts for the two of them that would restore efficiency.
4. In the following problem, X = G or X = B corresponds to the future weather pattern, and the prior distribution is P(X = G ) = 0.6. The possible actions are to Leave the infrastructure alone or to put in New infrastructure, and the signal, s, is the result of investigations and research into the distribution of future values of X. The infrastructure costs 4, and the utilities are
|
Good Bad
L 15 3
N (15 - 4) (10 - 4)
|
a. Give the optimal decision in terms of the beliefs/evidence βG = Prob(G).
b. Let us now suppose that we can run test/experiments that yield S = sG or S = sB with P(S = sG|G) = α ≥ 1/2 and P(S = sB|B) = β > 1/2.
The joint distribution, q(.,.), is
|
|
|
Good
|
|
Bad
|
|
sG
|
|
α - 0.60
|
|
(1- β) .40
|
|
sB
|
|
(1- α) - 0.60
|
|
β . 0.40
|
i. Give the posterior be iefs as a function of α and β.
ii. Show that if α = β = 1/2, the signal structure is worthless.
iii. Give the set of (α, β) ≥ (1/2, 1/2) for which the information structure strictly increases the expected utility of the decision maker.
c. Now suppose that the test/experiment can be run twice and that the results are independent across the trials. Thus, P(S = (sG,sG)|G) = α2, P(S = (sB,sG)|G) = P(S = (SB,SG)|G) = α(1 - α), and P(S = (sB, sa)|G = (1 - α)2 with the parallel pattern for B.
i. Fill in the probabilities in the following joint distribution q(.,.)
|
|
|
Good
|
|
Bad
|
|
(sG, sC)
|
|
|
|
|
| (sG, sB) |
|
|
|
|
| (sB, sG) |
|
|
|
|
| (sB, sB) |
|
|
|
|
ii. Verify that the average of posterior beliefs is the prior belief.
iii. Show that if α = β = 1/2, the signal structure is worthless.
iv. Give the set of (α, β) ≥ (1/2, 1/2) for which the information structure strictly increases the expected utility of the decision maker.