Reference no: EM131019263
Homework 5
1. First-degree Price Discrimination
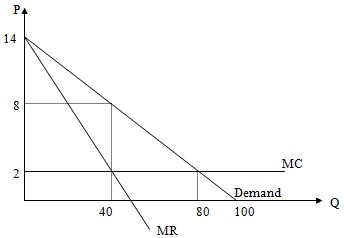
a. Assume that the above figure describes a perfectly competitive market. Find the equilibrium price and quantity, and the value of Consumer's and Producer's surplus (CS and PS). Is there a deadweight loss (DWL) when this good is produced in a perfectly competitive market?
b. Assume that the above figure describes a monopoly with no price discrimination. Find the equilibrium price and quantity. What is the value of the CS and PS in this case? Is there a deadweight loss (DWL) when this good is produced by a monopoly?
c. Now assume that the monopolist can use first-degree price discrimination (also called perfect price discrimination). What is the price of the last unit sold in the market and what is the total quantity traded? What is the value of CS and PS? What is the DWL in this case?
2. Identify which of the following statements describe first-degree, second-degree and third degree price discrimination.
(i) Charging different prices in separated markets
(ii) Adopting price schedules that give buyers an incentive to separate themselves into different price categories
(iii) Selling each unit at a different price, to the individual willing to pay the most for it.
3. Third-degree price discrimination
Suppose that the demand curves for a monopolist who sells their product in two separated markets are given by:
Q1 = 24 - P1, so marginal revenue for this market is given by
Q2 = 24 - 2P2 , so marginal revenue for this market is given by
A monopolist can serve both of these markets at a constant marginal cost of $6 (Fixed Cost is zero, so note that ATC=MC=$6).
a. What is the quantity that the monopolist will choose to supply in each market and what will be the price in each market?
b. Calculate the total profits for the monopolist.
For the next questions, assume that the monopoly has to pursue a single-price policy.
c. What is the market demand function?
d. For the single-price monopoly, marginal revenue for this market is given by MR = 16 -2/3Q. What is the equilibrium price and quantity?
e. Calculate profits. Compare these profits with the profits in the case where the monopolist could charge different prices.
4. Assume that a telephone company faces two types of consumers: the high-demand types who make a lot of phone calls each month, and the low-demand types who make only a small number of phone calls each month.
The company can charge the following price schedule: T=A+PQ, where A is a fixed amount paid by the consumer in order to be able to use the service during the billing period, P is the price paid for each additional phone call during the billing period, and T is the total price paid by the customer per billing period.
The firm has decided to offer two price schedules to the consumers:
T1=A1+P1Q and T2=A2+P2Q, where A1>A2 and P1<P2.
Can the firm choose A1, A2, P1, P2 such that high-demand types will choose one of the price schedules and low-demand types the other price schedule? If yes, which price schedule will each type choose?
[Monopolistically Competitive Market]
5. The beer market in Madison is monopolistically competitive. One of the beer companies faces the demand curve Qd = 100 - P. Total Cost for this firm is given as TC = 320 + 4Q + Q2 and marginal cost for this firm is MC = 4 + 10Q.
a. Derive the marginal revenue curve for this firm.
b. Draw the MR and MC curves for this firm in one graph.
c. What is the optimal quantity for this firm to produce?
d. Calculate the profit for this firm.
e. Predict what is going to happen in the long run to this firm and illustrate this long run outcome in a graph.
[Game Theory]
6. The following matrices describe payoff matrices for two players, P1 and P2. both players can choose "up" or "down".
a. From the matrix below, find out the dominant strategy for each player.
|
P1
|
P2
|
|
|
UP
|
Down
|
|
Up
|
1,1
|
4,6
|
|
Down
|
12,2
|
0,8
|
b. From the matrix below, find out the dominant strategy for each player.
|
P1
|
P2
|
|
|
UP
|
Down
|
|
Up
|
0,0
|
4,6
|
|
Down
|
0,2
|
1,0
|
c. From the matrix below, find out the dominant strategy for each player.
|
P1
|
P2
|
|
|
UP
|
Down
|
|
Up
|
10,10
|
4,6
|
|
Down
|
8,12
|
0,8
|
d. From the matrix below, find out the dominant strategy for each player. In this matrix, each player has three choices.
| P2 |
| P1 |
|
Left |
Center |
Right |
| Up |
6,1 |
47,12 |
5,0 |
| Middle |
3,15 |
35,17 |
0,8 |
| Down |
0,10 |
7,12 |
3,7 |
7. What will be the outcome, that is, what strategy will each player choose, in c) and d) in the question above.?
8. There are two firms in the market: OfficeMin and WorstBuy. Each firm can charge a regular price or a discounted price. When both firms charge the regular price on the item, each firm gets $500 as profit. But if one firm sets the discounted price on the item and other firm does not charge the discounted price, then the profit is $800 for the firm charging the discounted price and $200 for the firm charging the regular price. When both firms charge the discounted price, the profit is $300 for each firm.
a. Set up the payoff matrix for this game using the following table.
|
|
OfficeMin
|
|
Regular
|
Discount
|
|
WorstBuy
|
Regular
|
|
|
|
Discount
|
|
|
b. Which of the following is true?
(i) When OfficeMin chooses the discounted price, WorstBuy will choose the regular price.
(ii) When OfficeMin chooses the regular price, WorstBuy will choose the regular price.
(iii) Choosing the Discounted Price is a dominant strategy for WorstBuy.
(iv) Choosing the Regular Price is a dominant strategy for OfficeMin.
c. What do you predict will be the outcome from this game? That is, what strategy will OfficeMin pursue and what strategy will WorstBuy pursue?
9. Use the following matrix for the following questions.
|
A
|
B
|
|
|
Left
|
Right
|
|
Up
|
1,7
|
4,6
|
|
Down
|
9,3
|
x,y
|
A. For what value of x is "Down" a dominant strategy for A?
a) x<1.
b) x=0.
c) x<9.
d) x>4.
B. For what value of y is "Left" a dominant strategy for B?
a) y<3.
b) y>0.
c) y>6.
d) y<7.
C. Suppose x=5. For which value of y is (Down, Right) the chosen outcome for this game ?
a) y=0.
b) y=1.
c) y=2.
d) y=5.