Chemical Properties
(1) Formation of the oxides and hydroxides
(i) The elements (except Ba and Ra) when burnt in air give oxides of ionic nature M2+O2- which are crystalline in nature. The Ba and Ra though give peroxide. The affinity to form higher oxides increases from Be to Ra.
2M + O2 → 2MO (M is Be, Mg or Ca )
2M + O2 → MO2 (M is Ba or Sr)
(ii) Their less reactivity than the alkali metals is evident by the fact that they are slowly oxidized on exposure to air, though the reactivity of these metals towards oxygen increases on moving down the group.
(iii) The oxides of these metals are very stable due to high lattice energy.
(iv) The oxides of the metal (except BeO and MgO) dissolve in water to form basic hydroxides and evolve a large amount of heat. BeO and MgO have high lattice energy and hence insoluble in water.
(v) BeO dissolves both in acid and alkalies to give salts that is BeO possesses amphoteric nature.
BeO+2NaOH→Na2BeO2+H2O ; BeO+2HCl→BeCl2+H2O
Sod. beryllate Beryllium chloride
(vi)The basic nature of oxides of alkaline earth metals increases from Be to Ra as the electropositive Character increases from Be to Ra.
(vii)The affinity of these metal to react with water increases with increase in electropositive character that is Be to Ra.
(viii) Reaction of Be with water is not certain, the magnesium reacts only with hot water, while the other metals react with cold water but slowly and less energetically than the alkali metals.
(ix) The inertness of the Be and Mg towards water is because of the formation of protective, thin layer of the hydroxide on surface of the metals.
(x) The basic nature of the hydroxides increase from Be to Ra. It is due to increase in ionic radius down the group which results in the decrease in strength of M -O bond in M -(OH)2 to show more dissociation of the hydroxides and greater basic character.
(xi) The solubility of hydroxides of alkaline earth metals is relatively less than their corresponding alkali metal hydroxides in addition, the solubility of hydroxides of alkaline earth metals increases from Be to Ba. Be (OH)2 and Mg (OH)2 are nearly insoluble, Ca (OH)2 (generally called lime water) is sparingly soluble whereas Sr(OH)2 and Ba (OH)2 (generally called baryta water) are more soluble.
The trend of solubility of these hydroxides depends on the values of lattice energy and the hydration energy of these hydroxides. Magnitude of the hydration energy remains almost same while lattice energy decreases appreciably down the group leading to more negative values for DH solution down the group.
DH solution = DH lattice energy + DH hydration energy
More negative is DH solution more is solubility of compounds.
(xii) The basic character of the oxides and hydroxides of alkaline earth metals is lesser than their corresponding alkali metal oxides and hydroxides.
(xiii) The aqueous solution of lime water [Ca(OH)2] or baryta water [Ba(OH)]2 are used to qualitative identification and the quantative estimation of carbon dioxide, as both of them gives result to white precipitate with CO2 because of formation of insoluble CaCO3 or BaCO3
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O ; Ba(OH)2 + CO2 → BaCO3 + H2O
(white ppt) (white ppt)
SO2 also give white ppt of CaSO3 and BaSO3 on passing through the lime water or baryta water. Though on passing CO2 in the excess, white turbidity of the insoluble carbonates dissolve to provide a clear solution again due to the formation of soluble bicarbonates,
CaCO3 → H2O + CO2 → Ca(HCO3)2
(2) Hydrides
(i) Except Be, all alkaline earth metals form hydrides (MH2) on heating directly with H2 . M+ H2 → MH2.
(ii) The BeH2 is prepared by action of the LiAlH4 on BeCl2
2BeCl2 + LiAlH4 → 2BeH2 + LiCl + AlCl3.
(iii) The BeH2 and MgH2 are covalent whereas the other hydrides are ionic.
(iv) The ionic hydrides of Sr, Ca, Ba liberate H2 at the anode and the metal at cathode.
Fusion
CaH2 → Ca2+ + 2H-
Anode : 2H- → H2 + 2e- Cathode : Ca2+ + 2e- → Ca
(v) The stability of hydrides decreases from Be to Ba.
(vi) The hydrides possesing higher reactivity for the water, dissolves readily and produce the hydrogen gas.
CaH2(s) + 2H2O → Ca(OH) 2 + 2H2
(3) Carbonates and Bicarbonates
(i) All these metal carbonates (MCO3) are insoluble in neutral medium but soluble in the acid medium. These are precipitated by addition of the alkali metal or ammonium carbonate solution to the solution of these metals.
(NH4)2 CO3 + CaCl2 → 2NH4Cl + CaCO3
Na2CO3 + BaCl2 → 2NaCl + BaCO3
(ii) Alkaline earth metal carbonates are obtained as white precipitates when calculated amount of carbon dioxide is passed through the solution of the alkaline metal hydroxides.
M(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) → MCO3(s) + H2O(l)
And the sodium or the ammonium carbonate is added to solution of the alkaline earth metal salt such as CaCl2.
CaCl2 (aq) + Na2CO3 (aq) → CaCO3(s) +2 NaCl(aq)
(iii) The solubility of carbonates of these kind of metals also decreases downward in group because of the decrease of hydration energy as the lattice energy remains almost unchanged as in case of sulphates.
(vi) The carbonates of these metals decompose on heating to give oxides, temperature of the decomposition increasing from Be to Ba. Beryllium carbonate is unstable in nature.
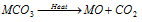
(4) Halides
(i) The alkaline earth metals combine directly with halogens at appropriate temperatures forming halides, MX2. These halides can be prepared by the action of halogen acids (HX) on metals, hydroxides metal oxides, and carbonates.
M + 2HX → MX2 + H2 ; MO + 2HX → MX2 + H2O
M(OH)2 + 2HX → MX2 +2H2O
MCO3 + 2HX → MX2 + CO2 + H2O
Beryllium chloride is however, conveniently obtained from oxide
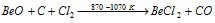
(ii) BeCl2 is essentially covalent, the chlorides MgCl2, CaCl2 , SrCl2 and BaCl2 are ionic; the ionic character increases as the size of the metal ion increases. The evidence is provided by the following facts,
(a) Beryllium chloride is relatively low melting and volatile whereas BaCl2 has high melting and stable.
(b) Beryllium chloride is soluble in organic solvents.
(iii) The halides of the members of this group are soluble in water and produce neutral solutions from which the hydrates such: MgCl2 6H2O, CaCl2.6H2O. BaCl2 2H2O can be crystallised. The affinity to form the hydrated halides decreases with the increasing size of metal ions.
(iv) The compound BeCl2 is readily hydrolysed with the water to form acid solution, BeCl2 + 2H2O → Be (OH)2 + 2HCl.
(v) The fluorides are relatively less soluble than the chlorides due to high lattice energies. Except the BeCl2 and MgCl2 chlorides of the alkaline earth metals impart characteristic colours to the flame.
CaCl2 SrCl2 BaCl2
Brick red colour Crimson colour Grassy green colour
Structure of BeCl2 : In the solid phase polymeric chain structure with three centre two electron bonding with Be-Cl-Be bridged structure is shown below,
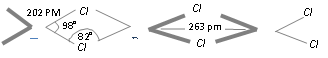
In the phase of vapour it tends to form a chloro-bridged dimer which dissociates into linear triatomic monomer at the high temperature at nearly 1200 K.
(5) Solubility in liquid ammonia : Like alkali metals, alkaline earth metals also dissolve in liquid ammonia to form coloured solutions When such a solution is evaporated, hexammoniate, M(NH3)6 is formed.
(6) Nitrides
(i) All the alkaline earth metals direct combine with N2 provides nitrides, M3N2.
(ii) The ease of formation of nitrides however decreases from Be to Ba.
(iii) Nitrides hear are hydrolysed water to liberate
NH3, M3N2 + 6H2O → 3M(OH)2 + 2NH3
(7) Sulphates
(i) All these form sulphate of the type M SO4 by the action of H2 SO4 on metals, their carbonates, oxides, or hydroxides.
M + H2SO4 → MSO4 + H2 ; MO+H2SO4 → MSO4+H2O
MCO3+ H2SO4 → MSO4 + H2O+CO2
M(OH)2 + H2SO4 → MSO4 + 2H2O
(ii) The solubility of sulphates in water decreases on moving down the group BeSO4 and MgSO4 are fairly soluble in water while BaSO4 is completely insoluble. This is because of increases in lattice energy of sulphates down the group which predominates over hydration energy.
(iii) Sulphate are quite stable to heat however reduced to sulphide on heating with carbon.
MSO4 + 2C → MS+2CO2
(8) Action with carbon : Alkaline metals (except Mg Be,) when heated along with carbon to form carbides of the type MC2 These carbides are also called acetylides as on hydrolysis they evolve acetylene.
MC2 + 2H2O→M(OH) 2 + C2H2
(9) Action with sulphur and phosphorus : Alkaline earth metals directly combine with sulphur and phosphorus when heated to form sulphides of the type MS and phosphides of the type M3P2 respectively.
M + S → MS ; 3M + 2P → M3P2
The sulphides on hydrolysis liberate gas H2S while phosphides on hydrolysis evolve the phosphine.
MS + dil. acid → H2S ; M3P2 + dil. acid → PH3
The sulphides are phosphorescent and are decomposed by the water
2MS + 2H2O → M(OH) 2 + M(HS)2
(10) Nitrates : Nitrates of these metals are soluble in the water. On heating them up they decompose into their corresponding oxides with the evolution of a mixture of nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
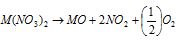
(11) Formation of complexes
(i) Tendency to show complex ion formation depends upon high nuclear charge, smaller size, and vacant orbitals to accept electron. As alkaline metals do not have these characteristics and thus are unable to form complex ion.
(ii) However, Be2+ on account of smaller size forms many complex such as (BeF3)1-, (BeF4)2-.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Chemical Properties of Alkaline Earth Metals questions? Chemical Properties of Alkaline Earth Metals topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Chemical Properties of Alkaline Earth Metals related problems. We provide step by step Chemical Properties of Alkaline Earth Metals question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Chemical Properties of Alkaline Earth Metals topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours