Resistance Temperature Effect
We know that resistance of a metallic conductor is given by
R = m/ne2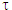 . l/A
. l/A
For a given conductor, R ∝ 1/ 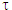
When the temperature of metal conductor is raised, the ions/atoms of the metal vibrate with greater amplitudes and greater frequencies about their mean positions (i.e. lattice sites). Due to increase in thermal energy, the frequency of collision of free electrons with atoms/ions while drifting towards positive end of the conductor time 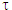 . Hence the value of resistance R increases with rise of temperature.
. Hence the value of resistance R increases with rise of temperature.
The resistance Rt of a metal conductor at temperature t° C is given by
Rt = R0 (1 + 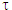 t + βt2)
t + βt2)
Where 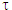 and β are temperature coefficients of resistance. R0 is the resistance of conductor at 0°C. their values vary from metal to metal. If the temperature t°C is not sufficiently large which is so in the most practical cases, the above relation may be expressed as
and β are temperature coefficients of resistance. R0 is the resistance of conductor at 0°C. their values vary from metal to metal. If the temperature t°C is not sufficiently large which is so in the most practical cases, the above relation may be expressed as
Rt = R0 (1 + 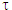 t) (1)
t) (1)
Or, Rt = R0 + R0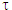 t.
t.
Or, 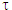 = Rt - R0/R0 × t
= Rt - R0/R0 × t
= increase in resistance/original resistance × rise of temp.
Thus temperature coefficient of resistance is defined as the increase in resistance per unit original resistance per degree rise of temperature.
For metals, like silver, copper etc. the value of 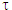 is positive because resistance of a metal increases with rise in temperature. The unit of
is positive because resistance of a metal increases with rise in temperature. The unit of 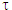 is K-1 or °C-1.
is K-1 or °C-1.
For insulators and semiconductors, 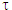 is negative, i.e. the resistance decreases with rise in temperature.
is negative, i.e. the resistance decreases with rise in temperature.
For alloys like manganin, eureka and constantan, the value of 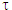 is very small as compared to that for metals. Due to high resistivity and low temperature coefficient resistance, these alloys are used in making standard resistance coils.
is very small as compared to that for metals. Due to high resistivity and low temperature coefficient resistance, these alloys are used in making standard resistance coils.
The value of 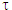 is different at different temperature. Temperature coefficient of resistance averaged over the temperature range t1 °C to t2 °C is given by
is different at different temperature. Temperature coefficient of resistance averaged over the temperature range t1 °C to t2 °C is given by
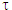 = (R2 – R1)/[R1(t2 – t1) (2)
= (R2 – R1)/[R1(t2 – t1) (2)
Resistance Temperature Effect Assignment Help, Resistance Temperature Effect Homework Help, Resistance Temperature Effect Tutors, Resistance Temperature Effect Solutions, Resistance Temperature Effect Tutors, Electrostatics Help, Physics Tutors, Resistance Temperature Effect Questions Answers