Reference no: EM13338918
There are a number of theories of the term structure of interest rates including the unbiased expectations hypothesis, preferred habitat hypothesis, and market segmentation hypothesis. Discuss the implications of the unbiased expectations hypothesis within the context of the following problem. Problem 1: For a two year, default free, zero coupon security, compute its yield to maturity and draw the respective yield curves assuming two different expectations of inflation employing the Fisher Effect and the data below:
(a) 4 percent one year from now, and
(b) 2 percent one year from now. In addition, define and compute the implied forward yield on a one year security one year from now, assuming the current two year yield is 6.0 percent.
Discuss the assumptions underlying this calculation and how it can be used to evaluate the implied forward yield on a 1-year loan, next year.
(c) What is the implied expected rate of inflation if the real rate remains at 3 percent?
Use the following definitions and values:
R = 0.03 (constant real rate of interest)
p1 = 0.02 (period 1 rate of inflation)
(a) p2e = 0.04 (expected period 2 rate of inflation)
(b) p2e = 0.02 (expected period 2 rate of inflation)
1y1 = current yield on one year securities
2y1e = Expected period 2 yield on one year securities
1y2 = current yield to maturity on two year securities
Unbiased Expectations Hypothesis
In general, (1 + 1ym) = [(1 + 1y1)(1 + 2y1e). . .(1 + my1e)]1/m and jy1e = the forward rate, jf1. Fisher Relationship: (1 + jy1) = (1 + jR1)(1+ jp1e ), where jp1e is the expected rate of inflation for period j for 1 year, and jR1 is the real rate of interest for period j for 1 year.
Specifically, (1 + 1y2) = [(1 + 1y1)(1 + 2y1e)]1/2 and 2y1e = the forward rate, 2f1.
The expected future 1-year yield factor is:
Don't forget to draw the yield curves under assumptions (a) and (b), above, for each of the expected rates of inflation. Give the reasons for the shapes of these yield curves (HINT: are forward rates on future short-term securities equal to, greater than, or less than current short-term interest rates).
1.2. Consider the following bank balance sheet (fixed rates and pure discount securities unless indicated otherwise). Interest rates on liabilities (yL) are 3 percent and on assets (yA) are 6 percent.
Duration
($millions) (years)
Super Now Checking Accounts (rates set daily) $150 1.5
6-Month Certificates of Deposit 50 .5
3-Year Certificates of Deposit 35 3.0
Total Liabilities 235 ?
Net Worth 20 -
Total Liabilities and Net Worth 255 -
Prime-Rate Loans (rates set daily) 75 1.0
2-Year Car Loans 100 1.5
30-Year Mortgages 80 7.0
Total Assets 255 ?
a. Find the duration of assets and liabilities.
b. Will the bank benefit or be hurt if all interest rates rise? Bank management can protect itself by (buying)/(selling) Treasury bond futures contracts. Explain by considering basis risk using interest rate futures to hedge a position with a variety of assets. How can the duration gap be managed through the use of financial futures contracts based on 10-year Treasury bonds? Define your terms and state clearly your assumptions.
c. Which asset is causing the substantial duration mismatch? Since the bank would take a capital loss if interest rates rose, what type of interest rate derivative contract would help hedge this possibility - buy a future or sell a future, and for what notional value?
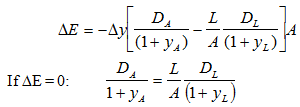
DE = change in the market value of equity,
DA = duration of assets,
DL = duration of liabilities,
L = market value of liabilities,
A = market value of assets, and
Dy = change
1. Mortgage markets have developed significantly since the early 1970s through the creation of secondary market instruments in the form of mortgage pass-throughs, collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOs), and REMICs. These collectively have been generally referred to as mortgage backed securities (MBS). In many ways, these instruments carry the characteristics of their underlying assets -- individual mortgages.
a. Why is the cash flow of a mortgage, or a MBS, uncertain in the sense that the investor in the mortgage has granted the borrower a call option to prepay the mortgage? Compare a mortgage cash flow with a Treasury coupon bearing bond paying interest semi-annually and a payment of principal at maturity.
b. What does this call option depend upon and why?
c. The cash flow for a mortgage pass-through typically is based on some prepayment speed benchmark. Why is the assumed prepayment speed necessary to price the MBS?
d. Suppose a bank has decided to invest in a MBS and is considering the following two securities: a Freddie Mac pass-through with a WAM of 340 months and an average life of 7 years or a PAC tranche of a Freddie Mac CMO issue with an average life of 2 years. In terms of prepayment risk, contraction risk and extension risk, which MBS would probably be best for the bank's asset/liability management perspective when it is known that liabilities generally have a duration less than 1 year and that assets have durations in the 2-year to 7-year range?
Average life is: 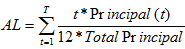
e. Compare the interest rate risk of a noncallable 10-year Treasury coupon bearing bond with a mortgage-backed pass-through security with prepayments related to the level of interest rates - lower market interest rates raise the rate of prepayments. Discuss how the changes in cash flows from a mortgage-backed security affect the duration of such securities. HINT: consider the coupon effect on duration.
Macaulay Duration Measure:
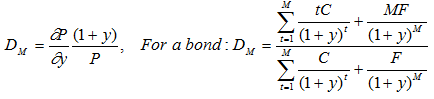
A more complete approximation to the proportional change in price of a bond with respect to a change in yield to maturity takes into account the convexity of the price-yield relationship for the bond:
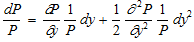
where P = Price, C = coupon, F = Face value, y = Yield to maturity, M = maturity (years), t = time (year), dP is the total change in price, and ∂P/∂y is the partial change in price with respect to a change in yield to maturity. The second term, excluding the dy2, is the convexity effect.
3.2. Are the following statements consistent or inconsistent? Explain your answer and discuss how equilibrium is achieved between the futures and cash markets.
1. Futures markets serve an important function of the global financial markets by giving investors the opportunity to better manage financial risks associated with their underlying business transactions.
2. The futures market is where price discovery takes place.
3. The introduction of futures contracts creates greater price volatility for the underlying commodity or financial asset.
3.3. Suppose the current yields to maturity on 3-month and 6-month T-Bills are 4.0 percent and 5.0 percent, respectively (yields will need to be converted to 90-day returns).
(a) In perfectly efficient markets and risk-neutral pricing, what yield should you expect to find on a 3-month T-bill forward contract deliverable in 3 months?
(b) Show that for the forward yield calculated in (a) the 6-month returns on (i) a 6-month spot bill and (ii) 3-month spot and 3-month futures bills are the same.
(c) Explain what factors would lead to a rejection of (b).
NOTE: From the term structure of interest rates recall:
(1 + oy2)2 = (1 + oy1)(1 + 1F1)
Where oy2 = the cash 6-month bill (two-period) yield,
oy1 = the cash 3-month bill (one-period) yield,
1F1 = the 3-month (one-period) forward yield one period from now.
ALSO, in the futures market:
(1 + oy2)2 = (1 + oy1)(1 + 1y1f),
where 1y1f = the 3-month futures yield on futures contracts due in three months.