Reference no: EM13316890
Question 1:
What do you think are the basic roles of the government in an economy? Why do you think that these roles of the government are justified?
The government plays a vital role in the economy in terms of allocation, redistribution and stabilization.
The allocation function, the responsibility of the government is to ensure that the resources of the society are used efficiently for the satisfactions of the wants of its members. Government has to provide for public goods such as national defense, government administration and so on to the people. These goods cannot be provided through market mechanism but are essential for consumers and therefore, the government has to provide them.
Also it regulates the externalities and allocates the regulations of business. Promote competitive markets or regulate market power and mostly protect individuals from information failures. Moreover, the distribution function of the government, it covers the activities involved in the redistribution of income. Distribution means the sharing of national income by individuals in a society, usually with the intension of realizing a fairer apportionment of consumption, income and wealth at the various levels of society.
Through its tax and expenditure policy government affects distribution of personal income of households in a manner which is just and fair. These include the improvements in health care facilities benefit to the sick, old and those to have children. Furthermore is the stabilization of the economy, example full employment, control of inflation and an equitable balance of payments is one of the goals that governments attempt to achieve through the management of fiscal and monetary policies. Fiscal policy related to taxes and expenditures while monetary policy is based on financial markets and the supply of credit, money and other financial assets.
Fiscal policy attempts to control the actions of individuals and companies by means of spending and taxation decisions. The government should spend money wisely on construction projects that stimulate other activity while on taxation; it can affect work, investment or production decision. Fiscal policy involves the government in deciding whether it should spend more than it receives or less and also the government attempt to guide the development of the economy by more specifically targeted policies. Monetary policy on the other hand is used to combat the inflationary rate, interest rate and deciding on the new money. In order to solve these, the central bank will then sell government securities thereby increasing interest rates and reducing the supply of private credit and money raise to discount rate, or increase reserve requirement.
Question 2:
Discuss how the size of a government can be measured. Comment on the statement, "A smaller size of the government implies less influence in the economy".
The size of the government can be measured by looking at the government's spending or revenues relative to the size of the state's economy. The appropriate measure of changes in state spending is one that assesses whether a given state can continue to provide existing services. Moreover it can also be measured by general expenditure is the sum of current and capital government expenditure on goods and services and transfer payments. The current expenditure includes public production of goods, purchase of goods from the private sector that are used for current consumption, contribution to statutory bodies and subsidies to public trading enterprises. Moreover the capital expenditure like funds used by a company to acquire or upgrade physical assets such as property, industrial buildings or equipment. This type of outlay is made by companies to maintain or increase the scope of their operation.
These expenditures can include everything from repairing a roof to building a brand new factory. Lastly is transfer payment; amounts that the government take from the amount of taxes that paid by tax payers to the recipients. For example in Samoa, old people get passion as their benefit from the government. More measure is expenditure is related to GDP which includes the productive capacity of the economy and GDP is usually measured at factor cost. General government final consumption expenditure (formerly general government consumption) includes all government current expenditures for purchases of goods and services (including compensation of employees). It also includes most expenditure on national defense and security, but excludes government military expenditures that are part of government capital formation. This can be used to measure how big is the government of whether the government is earning a profit or a loss.
It measures how big is the government in terms of it budget whether it is deficit or surplus. When the government spending is higher than it revenue, the government received deficit and therefore the size of the government is smaller which leads to less influence in the economy. Reducing inefficient government spending would benefit the economy, however, reducing efficient government spending would benefit the economy, however, reducing efficient government spending would harm it, and reducing the size of the government could involve either one.
Question 3
Discuss the incentives that might make private firms more efficient than state owned enterprises?
The only motive of private firms is to maximize profit. They have incentives to make them more efficient than state owned enterprises. Firstly is improved efficiency; the private companies have a profit incentive to cut costs and be more efficient. If you work for a government run industry, managers do not usually share in any profits.
However, a private firm is interested in making profit and so it is more likely to cut costs and be efficient. The worldwide spreads the idea that private ownership has more advantages than public in terms of being naturally and more profitable as well as constructing more optimal companies' capital structures. The increased focus in recent decades on a global scale on privatization process imposed a deeper and more consistent attention from researchers to look at this phenomenon.
To analyze the process of privatization, one does have to look to the motives that force this process to start. There are three main factors that give intention for privatization process. Firstly the financial reasons see privatization as additional source of financing which is the positive inflow for balancing public finances.
Secondly is political reasons is referring to distribution effects on society because privatization allows increasing the number of shareholders and provides access of citizens to capital markets. Last reason for privatization, which is the focus of this study is economic and is based on expectations that privatization leads to improvements in efficiency and also correspond to ideas. Argument that justifies superiority of privately owned entities against publicly owned, give reasons and main incentives for privatization to start. While analyzing privatization's impact on efficiency, one primarily has to address managerial problems.
The shift of ownership from public to private control has great impact on changes of management incentives, monitoring and lowers discretion in decision making. The difficulty of goals pursued by state owned entities itself give problems to monitoring their achievement.
The managers of privately owned entities main goal is defined as shareholders' wealth maximization, privatization leads to refocusing goals and implementation of strategies that help to achieve them. Moreover, the transfer from public sector with introduction of shares creates market for corporate control. If this market functions is in efficient way, then privatization should produce powerful incentives for increasing efficiency.
Private firms is influence through increasing competition in the industry, managers are in line competing with each other, what actually helps to increase managerial incentives.
Question 4
Show with appropriate use of diagrams how the market demand curve for a public good can be determined. Explain its efficiency conditions for efficient allocation of public goods and compare with the efficiency conditions necessary for the efficient provision of private goods.
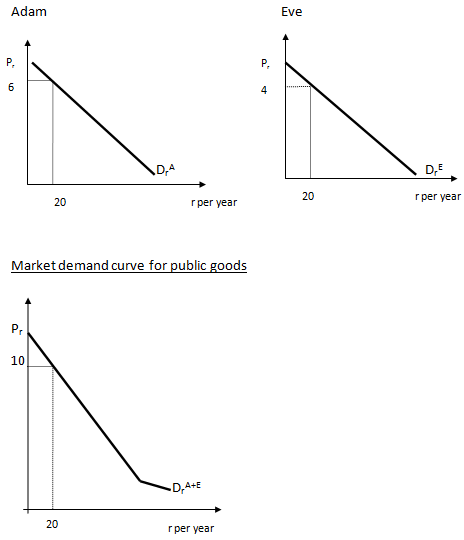
The market demand curve for a public good is obtained by the vertical summation of individual demand curves, which is in direct contrast to the market demand curve for private good obtained by the horizontal summation of individual demand curves. Since public good are non rival in consumption, market demand is obtained by summing the value that each consumer obtains from a given quantity. For private goods that are rivals in consumption, market demand is obtained by summing the quantity each consumer is willing to buy at a given price. For example in the textbook, it stated the two consumers Adam and Eve.
They enjoy display of fireworks. Firework display is a public good so when Eve's enjoyment of fireworks does not diminish Adam's and vice versa, and it is impossible for one person to exclude the other from watching the display. Since the size of the fireworks display can be varied and both Adam and Eve prefer bigger to smaller shows.
Assume the display consists of 19 rockets and can be expanded at a cost of $5 per rocket and Adam would be willing to pay $6 to expand the display by another rocket and that makes 20 rockets for the display. Eve would be willing to pay $4.
To find the market demand curve, the two individuals prices are sum up and we then we get $10 which is the market price while the quantity is remaining the same. This is why it says that market demand curve for public good is acquired from vertical summation.
|
|
Units of Fireworks
|
Price($)
|
|
Adam DAr
|
20
|
$6
|
|
Eve DEr
|
20
|
$4
|
|
Market DA+Er
|
20
|
$10
|
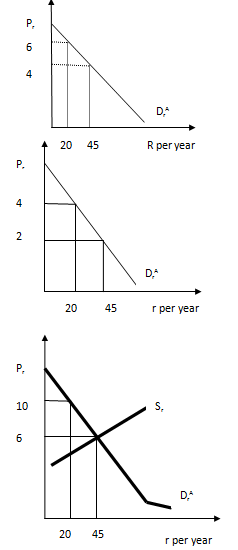
Furthermore, the comparison of marginal benefit which is the additional value associated with that rocket to the cost of providing that rocket which is marginal cost. The marginal benefit is 20th rocket is the sum of what Eve and Adam are willing to pay which is $10. The marginal cost is only $5 it pays to acquire the 20th rocket. If the sum of individuals' willingness to pay for an additional unit of a public good exceeds its marginal cost, efficiency requires that the unit be purchased, otherwise it should not. Hence, efficiency requires that provision of a public good be expanded until the point at which the sum of each person's marginal benefit for the last unit just equals the marginal cost. The efficient quantity of rockets is found where the sum of Adam's and eve's willingness to pay for an additional unit just equals the marginal cost of producing a unit. Adam's marginal willingness to pay for rockets is her marginal rate of substitution. Therefore the sum of the prices they are willing to pay equals MRSraAdam + MRSraEve. Therefore MRSraAdam + MRSraEve = MRTra. It is different from the conditions for efficiently providing a private good. Private good is when efficiency is required that each individual have the same marginal rate of substitution and that is equal the marginal rate of transformation. Whereas public good is the sum of the marginal rates of substitution must equal the marginal rate of transformation. Because everybody must consume the same amount of public good, its efficient provision requires that the total valuation they place on the last unit provided. Therefore the sum of MRSs equals the incremental cost of society of providing it.
Efficient provision of a public good
Efficient provision of a private good: The market is in equilibrium when supply and demand are equal.
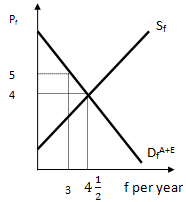
Question 5
It is often regarded that market based instruments are generally more efficient policies for dealing with externalities than government regulations. Discuss this statement by examining some specific issues by referring to some appropriate examples
Market-based instruments create incentives that encourage people, acting in their own self-interest, simultaneously to treat the environment in a way that is in the best interests of society. MBIs or market based instruments have two potential advantages over other types of instruments.
It allows different farm to make different adjustments in response to their unique business structures and opportunities. Also provide incentives to discover cheaper ways to outcomes thus reducing the future costs of achieving targets.
Market-based instruments are defined as aspects of laws or regulations that encourage behavior through market signals, rather than through explicit directives regarding pollution control levels or methods.
These policy instruments, such as tradable permits or pollution charges, can reasonably described as "harnessing market forces," because if they are well designed and properly implemented, they encourage firms or individuals to undertake pollution control efforts that are in their own interest and that collectively meet policy goals. On the other hand market instrument allow any desired level of pollution cleanup to be realized at the lowest overall cost to society by providing incentives for the greatest reduction in pollution by those firms than can achieve the reduction most cheaply.
For example, factories which give so much pollution in the environment paid a huge amount of tax which is called environmental taxes are taxes on proxies for pollution. In Samoa, there are factories which produce local products such as tobacco, Vailima beer and others. They pollute the air with it production by using the machines and production technology. Fortunately, the market-based demand instrument comes in and charges them with a tax in order to reduce down the pollution they caused. Market-based instrument policy is considered with four major categories: pollution charges, tradable permits, market friction reductions and government reductions.
Pollution charge systems assess a free or tax on the amount of pollution that a firm or source generates. Some countries such as USA considered the environmental user charges for those who are using the environment negatively. Moreover are tradable permits that can achieve the same cost-minimizing allocation of the control burden as a charge system while avoiding the problems of uncertain responses by firms and the distributional consequences of taxes. Some other ways, each factory or companies have pollution permits. They can trade out with one another when one factory needs to produce more products but their permit is limited. They buy the other firm's permit in order to do so. This is called trade out permit.