The Web Semantics Technology
Introduction
Today, the data we get from the web is in the form of web pages ie.,HTML documents that are associated with one another through the use of hyperlinks. Users and computers can read such documents, but extracting the meaning from them is not possible. Hence the W3C(World Wide Web consortium) has extended the concept of the web through a standard that promotes common data formats and protocols. This led to the concept of the web semantics. Sir Tim Berners-Lee, the father of World Wide Web, coined the term semantic web. There are two main ideas behind this. First, to associate metadata with internet resource. Metadata is bits of information about something. For example the title of a book, author, contents, date etc., Second is the ability to reason this metadata.
World Wide Web V/s Semantic web
World Wide Web is a collection of documents interlinked with one another which can be transmitted from one computer to the other. Any person can contribute his/her ideas to it. The machine simply delivers the content. The user has to assemble relevant data himself. The semantic web is an enhanced form of presenting the metadata where the computer can process the data. This helps the user to get collective data instead of document.
Need for semantic web
The main idea behind web semantics is to make information from the web widely available to all and also to increase the effective utilization of that knowledge. Web semantic technology gives advanced options for browsing, sorting and analysing the data. Web semantic technology represents data in the format which enables the machine to come to suitable decisions.
So the semantic web seeks to change the landscape of the internet in a number of ways:
* Making available the web of data to artificial intelligence processes (getting the web to do a bit of thinking for users).
* Encouraging companies, institutions, and users to publish their data without hesitation, in an open standard format.
* Encouraging businesses to use data already present on the web.
Web semantics can be understood under three phases
1. Model : A scientific model describes the real life aspects in a simple manner.
2.Computing: the gathered information is analysed to draw conclusions and decisions.
3.Information exchange: the metadata(data within data) is shared with users.
Ontology and semantics:
Ontology is the formal specification of an abstract concept. It is useful for knowledge sharing and reuse. The formal representation of ontology requires modelling. Two types of models are mentioned here.
i. Frame-based model: This uses frames,slots and facets as elements. The frame can represent any entity in a domain. A class frame represents a class and an individual frame represents an individual. One frame can inherit the properties of the other. Each frame has slot value. The frames, slots are given standard names depending on frequently used entities.
ii. Semantic network model: This is a graph, in which vertices represent concepts and edges represent the relation between them. Semantic network expresses vocabulary that is helpful particularly for human, but that can be used for machine processing.
Few of the common terms used in semantic networks are :
- If an entity A gives the same meaning as entity B is called a synonym
- If an entity A gives opposite meaning of entity B it is called an antonym
- If an entity gives a part of relation between two things then it may be called a meronym or holonym
- If the semantic range is included between the concepts in both directions then it may be called hyponym or hypernym
The Web Semantics Architecture
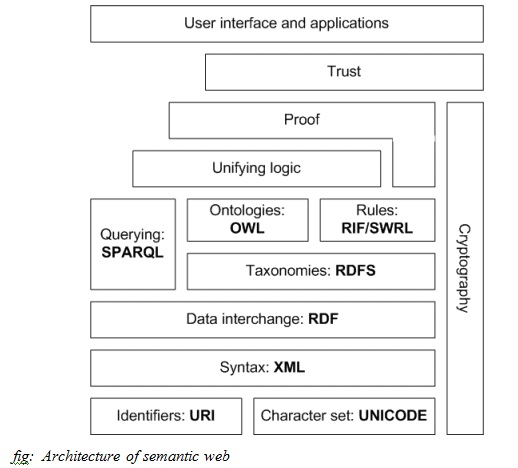
fig: Architecture of semantic web
The first layer consists of URI and Unicode which inherit the important features of World Wide Web. Unicode is a standard for encoding international character sets and it enables all human languages to be used (written and read) on the web using one standardized form. Uniform Resource Identifier (URI)is a string of a standardised form that allows to uniquely identify resources (e.g., documents). A subset of URI is Uniform Resource Locator (URL), which has a mechanism for data access and a (network) location of a document.
Extensible Markup Language(XML) forms the next layer which ensures common syntax in the semantic web. To represent the metadata in core format we use the information in graphical format.
RDF is a well-known model for data exchange on the internet. RDF has features that enable combining the data even if the schemas differ, and it supports the evolution of schemas without necessarily changing the data users.
RDF expands the linking structure of the Web to use URIs to name the relation between entities and two ends of the link. Using this simple model, it allows structured and semi-structured data to be combined, published, and shared across different applications.
This linking structure forms a graph with label and direction. Each graph has nodes and edges,where nodes represent resources and the edges represent the named link between two resources. This graph is the simplest possible model formed in mind for RDF and is often used in simplified visual explanations. RDF Schema is available to create lightweight ontologies. Unlike HTML and XML this allows further processing and recombination of data.
The web semantics language-OWL
The shortcomings of RDF led to the development of the language OWL. It is the combination of DAML(DARPA Agent Markup Language) and OIL(Ontology Interface layer). To create more detailed ontology OWL can be used, which is a language based on description logics and provides more constructs over RDFS and extra vocabulary. Due to its versatility, OWL became the official ontology language.
Other few available languages worth mentioning are SKOS and SPARQL.
SKOS: SKOS is an area of work developing specifications and standards to assist knowledge organization systems (KOS) such as thesauri, schemes for classification, subject heading systems, and naming structures within the framework of the Semantic Web.
SPARQL- this is a query language for RDF used to express queries and can also be used for value testing.
Conclusion
In a nutshell web, semantic technology enables the computer to read and understand the information, making it even more intelligent. The models and architecture are easy to understand and implement. Thus semantic web is superior to the previous ways of handling metadata. The effectiveness of this technology is obvious. The increased number of users and their satisfactory feedbacks and growing popularity of World Wide Web have made the efforts of developing web semantics a success.