New challenges require new technologies to tackle them. Here, the World Economic Forum's Global Agenda Council on Emerging Technologies identifies the top ten most technology trends that can help to deliver sustainable growth in decades to come as global population and material demands on the environment go on to grow rapidly. These are technologies that the Council considers have made development get through and are nearing large-scale employment.
Online Electric Vehicles (OLEV)-
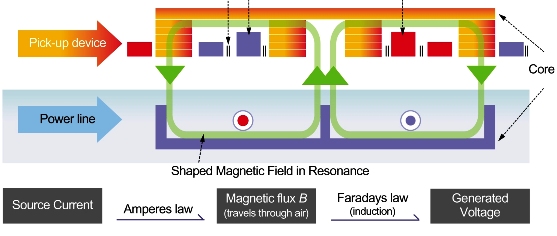
Wireless technology can at the present deliver electric power to moving vehicles. In next-generation electric cars, lift-up coil sets under the vehicle floor receive power remotely via an electromagnetic field broadcast from cables installed under road. The current also charges an onboard battery used to power vehicle while it is out of range. As electricity is supplied externally, these vehicles require only a fifth of the battery capacity of a standard electric car, and can achieve transmission efficiencies of over 80 percent. Online electric vehicles are at present undergoing road tests in Seoul, South Korea.
3-D printing and remote manufacturing-

3-dimensional printing allows the formation of solid structures from the digital computer file, potentially revolutionizing the economics of manufacturing if objects can be printed remotely in the home or office. The method involves layers of material being deposit on top of each other in to create free-standing structures from the bottom up. Blueprints from computer-aided design are sliced into cross-section for print templates, allowing virtually created objects to be used as models for hard copies completed from plastics, metal alloys or other kinds of materials.
Self-healing materials-

One of the important characteristics of living organisms is their inherent capability to repair physical damage. An increasing trend in biomimicry is the creation of non-living structural materials that also have the capacity to heal themselves while cut, torn or cracked. Self-healing materials that can repair damage without external human intervention might give manufactured goods longer lifetimes and reduce the requirement for raw materials, in addition to improving the inherent safety of materials used in construction or to form bodies of aircraft.
Carbon dioxide conversion and use-
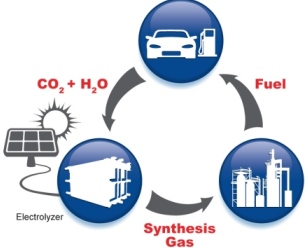
Long-promised technologies for the capture and underground sequestration of carbon dioxide have yet to be proven commercially viable, still at the scale of a single large power station. New technologies that change the unwanted CO2 into saleable goods can potentially address both the energetic and economic shortcomings of conventional CCS strategies. One of the most promising facts uses biologically engineered photosynthetic bacteria to turn waste CO2 into liquid fuels or chemicals in low-cost, modular solar converter systems. Individual systems are likely to reach hundreds of acres within two years. Being 10 to 100 times as creative per unit of land area, these systems address one of the major environmental constraints on biofuels from agricultural or algal feedstock and may well supply lower carbon fuels for automobiles, aviation or other big liquid-fuel users.
Fourth-generation reactors and nuclear-waste recycling-
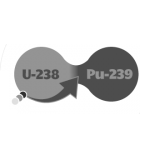
Present once-through nuclear power reactors use only 1 percent of the potential energy available in uranium, leaving the rest radioactively contaminated as nuclear waste. As the technical challenge of geological disposal is manageable, political challenge of nuclear waste critically limits the appeal of this zero-carbon and highly scalable energy expertise. Spent-fuel recycling and breeding uranium-238 into new fissile material known as Nuclear 2 would extend already-mined uranium resources for centuries even as dramatically reducing volume and long-term toxicity of wastes, whose radioactivity will drop below the level of the unique uranium ore on a timescale of centuries rather millennia. This makes geological disposal much less of a test and nuclear waste a minor environmental issue evaluated to hazardous wastes produced by other industries. Fourth-generation technologies, including liquid metal-cooled fast reactors are now being deployed in some countries and are offered by recognized nuclear engineering companies.
Remote sensing-
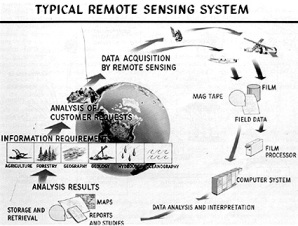
The more and more widespread use of sensors that allow frequently passive responses to external stimulate will continue to vary the way we respond to the environment, mainly in the area of health. Examples include sensors that continually monitor bodily function for example heart rate, blood oxygen and blood sugar levels and if necessary, triggers a medical response for instance insulin provision. Advance relies on wireless communication between devices, low power-sensing technologies and sometimes active energy harvesting. Other examples include vehicle-to-vehicle sensing for enhanced safety on the road.