Noise
In the wireless system, the term noise refers to an electromagnetic field which usually has large bandwidth; which means, it occurs over a wide range of frequencies and wave lengths. Noise does not convey information. It can be natural or human made.
It’s never good news
Noise never helps, and degrades, the performance of a wireless system. It is a concern in any device or system in which the data is sent from one place to another. The higher the noise level, the stronger a signal should be if it is to be received error free. At any given signal power level, higher noise levels translate into more errors and reduced communications range.
Figure given below is a spectral display of the signals and noise, having amplitude as a function of frequency. The device which generates this display is called as spectrum analyzer. The horizontal axis shows frequency; vertical axis shows amplitude. The background noise level is called as noise floor. Signals above noise floor appear in display and can be received. The strongest signals are received with fewest errors; weak signals are subject to most errors. Signals below noise floor are not displayed and cannot be retrieved unless a more sophisticated receiving system is used, or transmitter power output is increased, or both.
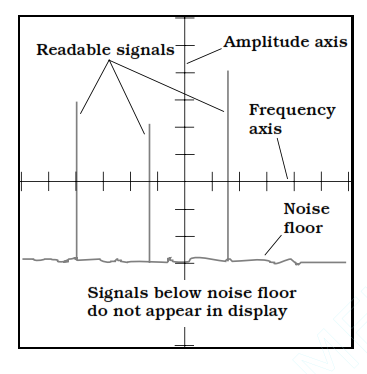
Figure--A spectrum-analyzer display. The vertical axis signifies amplitude, and the horizontal axis signifies frequency.
Minimizing noise
The noise level in electronic system can be minimized by using components which draw the least possible current. Noise can be kept down by lowering the temperature tremendously. Some experimentation has been done at cold temperatures; this is called as cryotechnology.
The narrower bandwidth of signal, the better signal to noise ratio will be, if all other factors remain constant. But this takes place at the expense of data speed. When noise originates mainly in sources outside wireless equipment (for instance, atmospheric static), reducing the bandwidth of receiving equipment is necessary. This means that, in the wireless communications with high external noise levels, the data speed should usually be slower than it would be if there was little external noise.
A noise limiter or a noise blanker can sometimes offer better communications without reducing the speed of data. Noise limiters chop off high-amplitude noise peaks, and blankers in effect turn receiver off during noise pulses. Such circuits are effective against human made impulse noise, characterized by high amplitude peaks of short duration. But thermal, solar, atmospheric, and galactic noise, which are essentially random, are not affected by limiters and blankers.