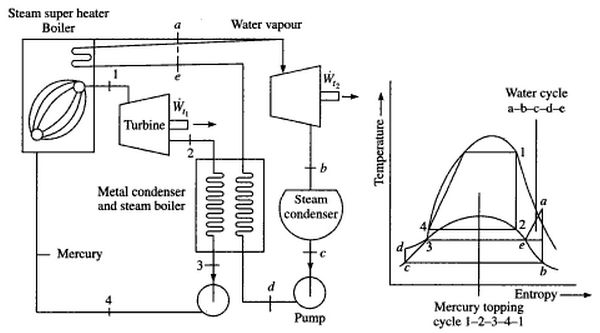
Vapor Power Cycles
In any thermodynamic procedure, the use of working fluid gas or vapor is a necessary working medium to translate heat into work. A cycle that continuously translates heat into work is termed as the power cycle. In a power cycle, the working fluid executes the different procedures that are compression, suction, expanding, condensing, and so on. All such procedures are performed constantly to produce work or converting heat into work. When the steam is alternatively vaporized and condensed, then the working cycle is termed as vapor power cycle.
There are different kinds of working fluids accessible like sodium, steam, potassium and mercury. Some working fluids are employed at high temperatures and some are at low temperatures. The steam is the mostly employed working fluid in the vapor power cycles. The steam has different desirable characteristics like low cost, easy accessibility and high enthalpy of vaporization.