Metabolism of galactose:
The hydrolysis of the disaccharide lactose (in milk) yields glucose and galactose. Thus galactose is also a main dietary sugar for humans. Glucose and Galactose are epimers which differ in their configuration at C-4. Therefore the entry of galactose into glycolysis needs an epimerization reaction. This occurs through a four-step pathway known as the galactose-glucose interconversion pathway show in the above figure:
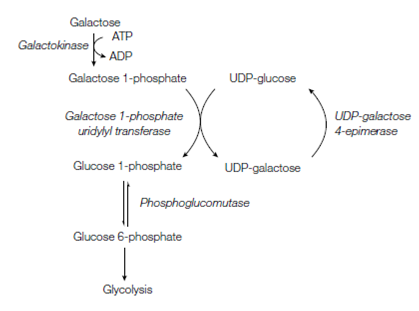
Figure: The galactose-glucose interconversion pathway.
1. Galactose is phosphorylated through galactokinase to provide galactose 1-phosphate.
2. Galactose 1-phosphate uridylyl transferase catalyzes the transfer of a uridyl group from UDP-glucose to galactose 1-phosphate to built glucose 1-phosphate and UDP-galactose.
3. The UDP-galactose is converted back to UDP-glucose through UDP-galactose 4-epimerase. Therefore, whole, UDP-glucose is not consumed in the reaction pathway.
4. At last the glucose 1-phosphate is transformed to glucose 6-phosphate through phosphoglucomutase. The glucose 6-phosphate then goes in glycolysis.
Galactosemia is a genetic disease caused through an inability to convert galactose to glucose. Toxic substances accumulate like as galactitol, formed through the reduction of galactose and lead to dire consequences for the individual. The Children who have the disease fail to thrive should vomit or have diarrhea after drinking milk and frequently have an enlarged liver and jaundice. The configuration of cataracts in the mental retardation and eyes and an early death from liver damage are also probable.
Most cases of galactosemia are due to a deficiency of the galactose 1-phosphate uridylyl transferase enzyme and therefore these individuals cannot metabolize galactose. The disease is treated through prescribing a galactose-free diet that causes all the symptoms to regress except mental retardation that may be irreversible. Because such patients have normal levels of UDP-galactose 4-epimerase, they can since synthesize UDP-galactose from UDP-glucose and so can since synthesize, for instance, oligosaccharides in glycoproteins which include Gal residues.