Anisotropy of chemical bonds:
Chemical shift is dependent on the orientation of the NMR active nucleus along with respect to the neighbouring bonds especially the π bonds. In such cases the circular motion of π electrons in the presence of applied magnetic field generates induced magnetic field which is anisotropic in nature. Anisotropic means that for some part of the molecule the field opposes the applied field and for other parts it augments the applied field. Let us know this with the help of the example of carbonyl group. An induced magnetic field for this group is display in Figure.
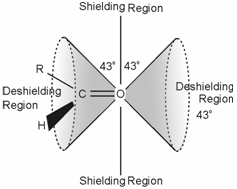
Figure: Anisotropic shielding and deshielding around a carbonyl group
There are two cone shaped volumes that lie parallel to the C=O bond axis. These are the deshielding regions and any proton falling in these regions would come to resonance at low fields or high δ value. The high chemical shift (~ 9.2 ppm) of the aldehydic protons is a typical example. The protons which are outside the region of these cones would be shielded from the applied field and accordingly come to resonance at high field.