The diode tube
Before the twentieth century started, scientists knew that the electrons could carry a current through a vacuum. They knew that hot electrodes would emit electrons much easily than cool ones. These phenomena were put to use in 1st electron tubes, called as diode tubes, for purpose of rectification.
Cathode, filament, plate
In any of the tube, the electron-emitting electrode is called as cathode. The cathode is usually heated by a wire filament, similar to glowing element in an incandescent bulb. The electron collecting electrode is called as anode or plate.
Directly heated cathode
In some tubes, the filament also serves as the cathode. This is called a directly heated cathode. The negative supply voltage is applied to the filament directly . The filament voltage for most of the tubes is 6 V or 12 V. The schematic symbol for the diode tube with a directly heated cathode is shown below.
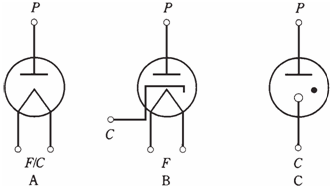
Figure--Schematic symbols for diode tubes; C = cathode, F = filament, P = plate. At point A, directly heated cathode; at point B, indirectly heated cathode; at point C, cold cathode.
Indirectly heated cathode
In many tubes, filament is enclosed within the cylindrical cathode, and cathode gets hot from infrared radiation. This is called as an indirectly heated cathode. The cathode is grounded itself. The filament receives 6 V or 12 Vac. In the directly heated or indirectly heated cathode, electrons are driven off the element by heat of the filament. The cathode of a tube is therefore somewhat analogous to the source of a field effect transistor, or to emitter of a bipolar transistor.As the electron emission in a tube depends on filament or heater, tubes require a certain amount of time normally 30 seconds to a few minutes to warm up.
This waiting period can be a big annoyance, and it seems bizarre at 1st to people who have not dealt with the tubes before.
Cold cathode
In the gas-filled voltage-regulator tube, the cathode may not have a filament to heat it. This type of device is called as cold-cathode tube. The schematic symbol for the cold cathode tube is shown in the figure given below. The solid dot indicates that tube is gas filled, instead of completely evacuated. Various chemical elements are used in gas filled tubes; mercury vapor is most common. In this type of tube, the warm up period is the time required for elemental mercury to vaporize, usually a couple of minutes.
Plate
The plate, or anode, of the tube is a cylinder concentric with cathode and filament. The plate is connected to positive direct current supply voltage. Tubes characteristically operate at around 50 V to more than 3 kVdc
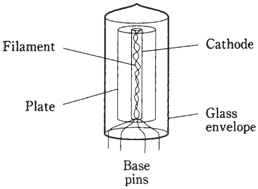
Figure--Construction of diode tube.For clarity, electrodes are shown transparent. In fact they are opaque metal.
As the plate readily attracts electrons but is not a good emitter, and because the exact opposite is true of cathode, a diode tube works well as rectifier for an ac. Diode tubes can work as envelope detectors also for AM, although they are no longer used for that purpose now.