Superimposed direct current
Sometimes a wave can have components of both ac and dc. The simplest example of an ac/dc combination is illustrated by the connection of a dc source, such as a battery, in series with an ac source, like the utility mains. An instance is shown in the schematic diagram of figure. Imagine connecting a 12-V automotive battery in series with wall outlet. Then the alternating current wave will be displaced either positively or negatively by 12 V, depending on polarity of the battery. This will result in the sine wave at output, but 1 peak will be 24 V more than the other peak.
Any ac wave can have direct current components along with it. If the direct current component exceeds the peak value of the alternating current wave, then fluctuating, or pulsating, direct current will result. This would happen, for instance, if a 200-Vdc source were connected in series with utility output. Pulsating direct current would appear, with an average value of 200 V but with instantaneous values quite higher and lower. The waveshape in this case is shown in the figure given below.
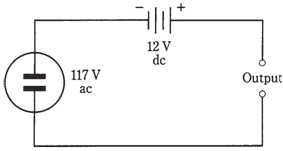
Figure-- Connection of a dc source in series with an ac source.
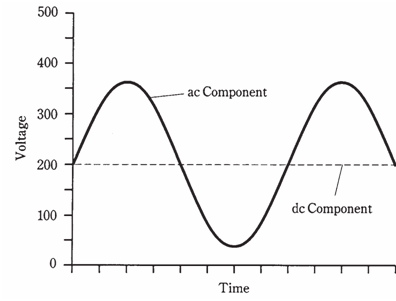
Figure-- Waveform resulting from 117 Vac in series with + 200 Vdc.
Hybrid ac or dc combinations are not generated deliberately. But such wave- forms are at times seen at certain points in the electronic circuitry.