Marginal utility approach
The downward sloping nature of the demand curve can be explained by using the law of diminishing marginal utility. For instance, consider a consumer who ahs to choose between two goods, X and Y, which have prices Px and Py respectively. Assume that the individual is rational and so wishes to maximise total utility subject to the size of the income.
The consumer will be maximising total utility when his or her income has been allocated in such a way that utility to be derived from the consumption of one extra shillings worth of X is equal to the utility to be derived from the consumption of one extra shillings worth of Y. In other words, when the marginal utility per shilling of X is equal to the marginal utility per shilling of Y. Only when this is true will it not be possible to increase total utility by switching expenditure from one good to another. This condition for consumer equilibrium can be written as follows:
Mux = Muy
Px Py
Where MUx and MUy are the marginal utilities of X and Y respectively and Px and Py are the
prices (in shillings) of X and Y respectively.
Any number of commodities may then be added to the equation. The table below gives hypothetical marginal utility figures for a consumer who wishes to distribute expenditure of K£44 between three commodities X, Y and Z.
Marginal utilities derived from each Kg of:
|
Kg consumed
|
x (£8/kg)
|
Y (£4/kg)
|
Z (£2/kg)
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
72
48
40
36
32
20
12
|
60
44
32
24
20
8
4
|
64
56
40
28
16
12
8
|
In order to maximize utility, the consumer must distribute available income so that:
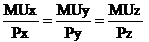
From the table you can see that this yields, a selection where the consumer buys 2 kg of X, 4 kg of Y and 6 kg of Z. Hence:
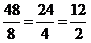
If the consumer wishes to spend all the K£44, it is impossible to distribute it any other way which would yield greater total quality. This theorem is called the concept of equi-marginal utilities.