Q. Explain the three-line cable Residential wiring?
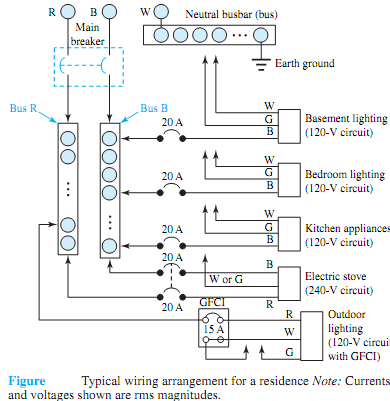
The three-line cable coming out of the secondaries of the distribution transformer on the utility pole passes through the electric meter that measures energy consumption in kilowatt-hours and terminates at the main panel. Figure 4.4.2 shows a typical wiring arrangement for a residence. At the main panel, circuit breakers serve the joint role of disconnecting switches and overcurrent protection; the neutral is connected to a busbar (bus) and in turn to the local earth ground; the hot lines are connected to individual circuits for lighting and appliances, as illustrated in Figure.
The circuit breaker labeled GFCI (ground-fault circuit interruption), used for safety primarily with outdoor circuits and in bathrooms, has additional features that will be described later. Note that every outgoing "hot" wire must be connected to a circuit breaker, whereas every neutral wire and ground wire must be tied directly to earth ground at the neutral busbar.
Today most homes have three-wire connections to their outlets, one of which is shown in Figure. The need for both ground and neutral connections needs to be explained, since the ground conductormay appear to be redundant, playing no role in the actual operation of a load that might be connected to the receptacle. From the viewpoint of safety, the ground connection is used to connect the metallic chassis of the appliance to earth ground. Without the ground conductor connected to the metal case of the appliance, as shown in Figure(a), the appliance chassis could be at any potentialwith respect to ground, possibly even at the "hot"wire's potential if a part of the "hot" wire were to lose some insulation and come in contact with the inside of the chassis.
An unintended connectionmay occur because of the corrosion of insulation or a loosemechanical connection. Poorly grounded appliances can thus be a significant hazard by providing a path to ground through the body of a person touching the chassis with a hand. An undersized ground loop current limited by the body resistance may flow directly through the body to ground and could be quite harmful. Typically, the circuit breaker would not operate under such circumstances.