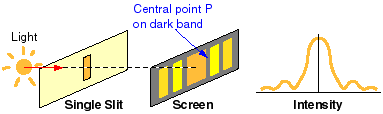
Explain the meaning of Diffraction
The spreading of a wave around a corner or through a slit of width b, which is about an order of magnitude of the size of the wavelength, is called diffraction. Light that is passed through a narrow slit produces a central bright band with parallel bands to both sides which are about 1/20 the brightness of the central band.
Animations of various kinds of diffraction can be observed here. Notice what happens when two waves coincide! Areas of overlap indicate constructive interference.
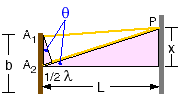
The middle of the first dark band is located where the path difference between the light coming from the center of the slit and from one edge of the slit is θ of the light's wavelength.
if d << L so that θ ˜ sin θ
Sin θ = x/L = ½ λ / ½ b = λ /b
You can see this effect pretty easily if you hold your first and second finger close to one eye (close the other eye) and parallel to each other. Then while looking at a bright area (preferably not a very small bright light), squeeze your two fingers closer and closer together until you see stripes parallel to your fingers as the slit becomes very thin.
Because the amount of bending or spreading changes with the wavelength (more bending of blue wavelengths and less bending of red wavelengths) of the light, if the slit is thin enough and repeated many times to make a very fine grating, this effect can make rainbows out of white light by spreading out the many colors which make up white light. The funky glasses that make you see rainbows everywhere are made of transparent, very fine diffraction gratings. The "holographic" and "prismatic" stickers use diffraction gratings to create rainbows as well.
Holograms are specialized interference patterns recorded on a thin film emulsion on glass or plastic, enabling your eyes to see exactly the pattern of light waves that was reflected by a three- dimensional object. By using very coherent light - that is, single frequency and no variation in phase across the beam so the beam will not interfere with itself - and keeping the optical elements very still with respect to each other, a very precise interference pattern is recorded on film. When this film is developed and viewed at the proper angle, the interference pattern on the film recreates the light waves which were reflected by the object, giving you a sense of seeing the three-dimensional object itself, even though the object is no longer there.