Determinants of Money Supply
The preceding sections concentrate on the processes through which the commercial banking system creates and destroys deposits by purchasing and selling assets of various kinds. As far as the supply of money is concerned, the net effect of this is summarized in the multiplier formula
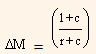 ΔH which expresses the change in the money stock ΔM as a function of the change in reserves ΔH, the reserve-requirement ratio, r, and the parameter relating to currency c. One danger with the multiplier approach is that it gives the impression that changes in the quantity of money are brought about by a rather mechanical process. In particular, our formula suggests that, given the reserve-requirement ratios, the Reserve Bank simply picks ΔH and out pops ΔM . As we shall now see, for a variety of reasons this view is terribly misleading.
ΔH which expresses the change in the money stock ΔM as a function of the change in reserves ΔH, the reserve-requirement ratio, r, and the parameter relating to currency c. One danger with the multiplier approach is that it gives the impression that changes in the quantity of money are brought about by a rather mechanical process. In particular, our formula suggests that, given the reserve-requirement ratios, the Reserve Bank simply picks ΔH and out pops ΔM . As we shall now see, for a variety of reasons this view is terribly misleading.
The Behavior of the Public
Part of the seeming simplicity of the multiplier formula stems from the way in which currency appears to affect changes in the supply of money. The influence of these two quantities is captured in the parameter 'c', innocently suggesting that these are institutionally determined constants. But, this is not so. Currency does not move hand in hand with demand deposits. Rather, the quantities of currency that the public chooses to hold vary over time in response to economic factors. In determining the quantities that it will demand of currency, demand deposits, and other financial assets, the public considers their relative liquidity and safety and their relative yields. Consequently, a change in any one of these factors can alter the willingness of the public to hold currency relative to demand deposits (i.e. the parameter 'c'. For instance, the growth of particular kind of transactions could alter the relative convenience of currency as compared with demand deposits.
In short, the parameter 'c' is an economically determined variable that cannot be expected to remain constant over the time. While in some circumstances it may change only slowly, if general economic conditions change rapidly 'c' may also exhibit sizeable changes in a relatively brief period.
Commercial Bank Behavior
Aside from bank-induced variations in the characteristics of their liabilities, the behavior of the commercial banks affects the interpretation of the multiplier formula in another very important way. In deriving the multiplier formula we have assumed that the commercial banks are able and willing to exercise their maximum lending power. Put another way, banks are assumed to utilize fully an injection of new reserves and not to add to their excess reserves. However, throughout many periods of our history this has not been the case. The reason is simple. Excess reserves serve a useful function in keeping a bank liquid so that it may meet adverse clearing balances or the loan demand of its valued customers. The desirability of holding excess reserves for such purposes depends on the cost of holding such reserves - the interest income forgone from holding a non-earning asset - relative to the anticipated costs of meeting a deficient reserve position or new loan demand.
Clearly, as with the case of 'c' given previously, this is an economic decision. We would expect that, other things being equal, the lower the interest rate on relatively liquid securities and hence the lower the opportunity cost on holding such reserves, the more excess reserves banks would hold. Evidently then, the implicit assumption in our formula of a maximum expansion of earning assets will not always be met.
Reserve Bank Influence
The remaining way in which the multiplier formula somewhat oversimplifies reality is the deceptive appearance of  , the quantity we have identified as the injection of new reserves. While we have suggested that the Reserve Bank can regulate the volume of reserves, it is not endowed with a 'reserve dial' that it simply sets to achieve a desired change in reserves. Rather, it must contend with a significant number of diverse factors that affect bank reserves. Among the various influences on the quantity of reserves are the following: changes in the gold stock, borrowing of reserves by the commercial banks, and the volume of foreign-owned deposits held at the Reserve Bank. Each of these factors can be only imperfectly anticipated by the Reserve Bank, so that the task of regulating the volume of reserves is far from a mechanical one.
, the quantity we have identified as the injection of new reserves. While we have suggested that the Reserve Bank can regulate the volume of reserves, it is not endowed with a 'reserve dial' that it simply sets to achieve a desired change in reserves. Rather, it must contend with a significant number of diverse factors that affect bank reserves. Among the various influences on the quantity of reserves are the following: changes in the gold stock, borrowing of reserves by the commercial banks, and the volume of foreign-owned deposits held at the Reserve Bank. Each of these factors can be only imperfectly anticipated by the Reserve Bank, so that the task of regulating the volume of reserves is far from a mechanical one.
Other Factors
There are a number of other respects in which the money-multiplier formula presented as equation is somewhat simplified.
One of the complications with the multiplier formula concerns the definition of money. For instance, some economists might argue that we should use a broader definition of the money stock, one that includes time deposits. Obviously, the precise form of the money multiplier will change if we adopt this definition. Alternatively, some economists might advance a definition of the money stock that included liabilities of financial intermediaries other than commercial banks. Once again, for any specific definition we could present an appropriate money multiplier. As before, however one would not use such a formula in a mechanical way. Rather, one would look at the economic forces that contributed to the development of non-bank liabilities as extremely close substitutes for money as it has traditionally been defined.
Though the multiplier formula should not be regarded as a mechanical tool, it plays an extremely useful role in highlighting how an injection (or withdrawal) of reserves will be translated into a change in the money supply. Indeed, when properly interpreted, it serves to emphasize the importance of asset choices by the public and the commercial banks in the money supply process. Furthermore, it makes clear that the Reserve Bank, should it desire to achieve some specific change in the money supply, must be able to forecast the consequences of the behavior of the public and the commercial banks. Such anticipation is necessary, above and beyond the somewhat more technical problems of controlling the quantity of reserves.