Q. Basic Architecture of computer system?
Replacing the ALU and CU (i.e., CPU) of Figure by a microprocessor, and storing instructions and data in the same memory, one arrives at a stored-program computer or a microcomputer. A bus, which is a set of wires carrying address, data, and control signals, is employed for interconnecting themajor components of amicrocomputer system.The address lines are unidirectional signals that specify the address of a memory location of an I/O device. With a typical 24-bit address bus, the microprocessor can access 224 (over 16 million) memory locations.
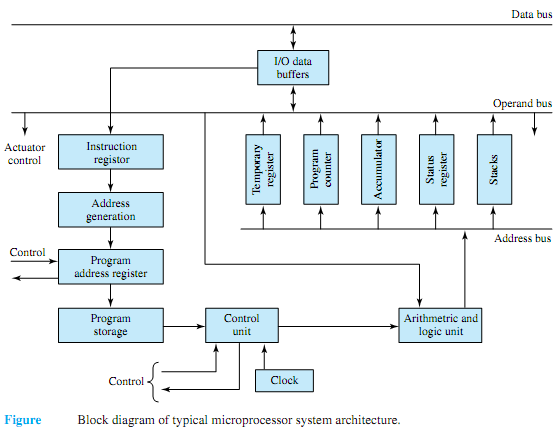
Memory is generally organized in blocks of 8, 16, or 32 bits. The data bus is a bidirectional bus, varying in size from 8 to 32 bits, which carries data between the CPU, MU, and I/O units. The control bus provides signals to synchronize the memory and I/O operations, select either memory or an I/O device, and request either the read or the write operation from the device selected. While there are virtually countless variations in microprocessor circuit configurations, the system architecture of a typical microprocessor is shown in Figure. The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) accepts data from the data bus, processes the data as per program-storage instructions and/or external control signals, and feeds the results into temporary storage, from which external control and actuator control functions can be performed. The accumulators are parallel storage registers used for processing the work in progress, temporarily storing addresses and data, and housekeeping functions. The stacks provide temporary data storage in a sequential order and are of use during the execution of subroutines. A subroutine is a group of instructions that appears only once in the program code, but can be executed from different points in the program. The program counter is a register/counter that holds the address of the memory location containing the next instruction to be executed. The status register contains condition-code bits or flags (set to logic 1 or logic 0, depending on the result of the previous instruction) that are used to make decisions and redirect the program flow. The control unit (CU), which consists of the timing and data-routing circuits, decodes the instruction being processed and properly establishes data paths among the various elements of the microprocessor. Interconnections may take the form of gates that the control section enables or disables according to the program instructions. That is to say, programming at the machine-language level amounts to wiring with software instead of hard-wired connections.