Reference no: EM13689608
1. Describe and give explanations for the following trends in period 3:
Melting / Boiling Point
Atomic radius
Radius of +1 cation
Radius of - 1 anion
2. Describe and give explanations (with equations where appropriate) for the following properties of Group I elements:
Oxidation State
Bonding nature of element
Bonding nature of compound
Reactivity of element with oxygen gas
Reactivity of element with chlorine gas
Reactivity of Group I hydroxides with hydrochloric acid
Reactivity of Group I carbonates with sulphuric acid
3. Describe and give explanations (with equations where appropriate) for the following properties of Group II elements:
Oxidation State
Bonding nature of element
Bonding nature of compound
Reactivity of element with oxygen gas
Reactivity of element with chlorine gas
Reactivity of Group II hydroxides with hydrochloric acid
Reactivity of Group II carbonates with sulphuric acid
4. Describe and give explanations (with equations where appropriate) for the following properties of Group VII elements:
Oxidation State
Bonding nature of the element
Bonding nature of compound
Reactivity of element with oxygen gas
Reactivity of element with elemental potassium
Reactivity of Group VII -1 ions with other group VII elemental compounds
5. Use oxidation and reduction terminology to explain and arrange the elements below in order of reactivity:
Al, Au, Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, Na, Pb, Zn
6. Use oxidation and reduction terminology to explain what happens when solid copper reacts with oxygen gas - you must produce half equations for oxidation and reduction
7. Use oxidation and reduction terminology to explain what happens when solid sodium reacts with water - you must produce half equations for oxidation and reduction
8. Explain the chemistry significance of the term "functional group".
9. Produce a table outlining Name, Functional Group, Melting Point, Water Solubility, Acidity for the following chemicals:
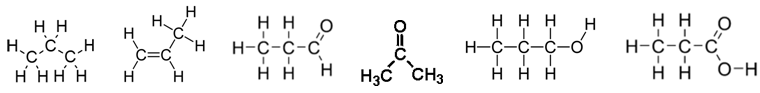
10. Draw and name 3 structural isomers of hexane
11. Draw and name 2 geometric isomers of pentene and explain why propene cannot display geometric isomerism
12. Draw two optical isomers of heptane and explain why there no isomers of propane that can display optical isomerism
13. Explain what kind of polymerisation occurs when:
a. Propene reacts with itself. b.Ethandioic acid reacts with propan-1,3-diol