Reference no: EM13434
Changes in government spending and interest rates.
Government spending is given by the equations:
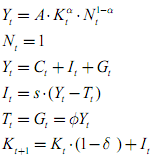
Recall that current government spending is a fraction Φ of current output. Suppose now that Φ is drawn randomly each period (sometimes the government needs a lot of resources other times it doesn't). Specifically, we will assume that Φ is uniformly distributed between [.17 and .23] (it has an average of .2). Set s = .2, δ = .1, α = .35 and A = .10
a.) Calculate steady state capital, (K*), output (Y*) and consumption (C*) assuming Φ = .2.
If consumers had "standard" preferences, the tangency conditions would imply
ct+1/ct = 1+ri
Since the interest rate is set before future consumption is realized, consumers have only expectations for ct+1. Assume consumers expect ct+1 to be equal to the steady state level of consumption C*. As a result, the real interest rate will satisfy:
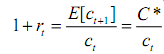
b.) Redo the spreadsheet program but create new columns for Φt, ct and (1 + rt). To have Excel draw random numbers between .17 and .23 type " = .17 + rand()*.06 " (note: Excel will redraw random numbers each time you hit enter or delete so don't get too attached to any one simulation). Plot out one simulation (e.g, plot Y, I and G).
c.) Add another column and calculate the % difference between 1+rt and the steady state value of 1+r (which is 1). Also calculate the % differences between Gt and the steady state value of G (which is .2Y*). These series are:
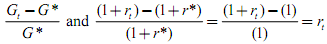
Plot these series (plot out 20 periods or so). What is the relationship between Gt and rt? Does this make sense?
2. IS/LM and Forward Looking Consumers.
The normal IS relationship is derived from the goods market clearing condition:
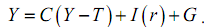
However, we know from our simple 2-period dynamic optimizing models that consumption does not just depend on current disposable income (Y -T), rather, the consumption function we used says that C = C (W- , Y - T, r) so that the IS relationship should be
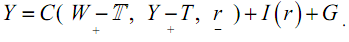
This is useful because it implies that expectations about future taxes and income (as they are incorporated into W and ) will affect C now.
Assuming that Ricardian Equivalence does not hold, use the IS/LM model with the modifications described above to describe how the following events would affect Y, C, I, and r.
a.) The President passes a "phased in" tax cut that will go into effect after a year.
b.) The public expects a substantial increase in government spending in the future.
c.) Consider the following two tax policies:
(A) raises taxes by ΔT this year but then returns taxes back to normal in the future.
(B) raises taxes permanently by ΔT.
Will these policies affect Aggregate Demand differently? How?
d.) How would Ricardian Equivalence change your answers?